
Check simplified square roots by calculating approximations of the answer using both the original problem and the simplified answer on a calculator to verify that the results are the same.Once a perfect square is found, apply the property a ⋅ b = a ⋅ b, where a and b are nonnegative, and simplify. Simplify a square root by looking for the largest perfect square factor of the radicand.
The principal square root is the positive square root.
RIGHT TRIANGLE CALCULATOR WITH SQUARE ROOTS PLUS
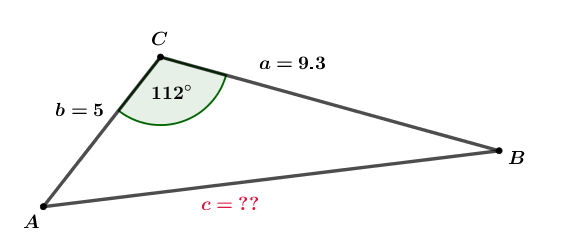
The hypotenuse c is equal to the square root of a squared plus b squared. The length of hypotenuse c can be found using the following formula: The length of leg b is equal to the square root of c squared minus a squared. The length of leg b can be found using the following formula: The length of leg a is equal to the square root of c squared minus b squared. The length of leg a can be found using the following formula: The following formulas are derived from the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any edge of a right triangle. To solve, replace the values of a, b, or c in the formula with the two known values and solve the equation. Given the length of any two edges of a right triangle, the Pythagorean theorem is used to solve the length of the third edge.
RIGHT TRIANGLE CALCULATOR WITH SQUARE ROOTS HOW TO
How to use the Pythagorean Theorem for Right Triangles Thus, the length of edge a squared plus the length of edge b squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse c squared. The Pythagorean theorem is expressed using the following equation: The Pythagorean theorem states that the length of the hypotenuse squared is equal to the sum of the squares of each leg. The Pythagorean theorem can be used to solve any side if the length of the other two sides is known.

The equation defines the relationship between the length of the three sides of a right triangle. The Pythagorean theorem, sometimes called Pythagoras’ theorem, is an equation used to solve the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
